| gRomK13 |
August 6, 2009 12:18 |
Pressure variation in a heating channel
Hello
I'd like to calculate the pressure variation between the inlet and the outlet of a heating channel. The causes of this variation are well known :
- Friction, because of viscosity and turbulence : IRREVERSIBLE
- Fluid Acceleration, either because of density change (heating for instance!) or because of cross section change : REVERSIBLE
- Gravity, if z coordinate changes : REVERSIBLE
Now I want to give an expression for these different components, but my two methods are not in agreement...
1) First Method: 1D Navier-Stokes
1D Momentum equation:
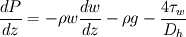 ( 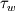 is wall friction, thus the whole term is the one responsible for friction pressure drop)
From which we define:
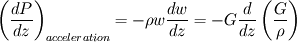
where 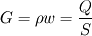 is mass velocity (Q is the mass flowrate and S is the cross section)
It comes: 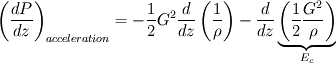
Then integration of a small portion of my channel gives: 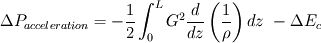 - When density is constant (no heating) and cross section varies: First term is zero, so that leaves us with
- When density is constant (no heating) and cross section varies: First term is zero, so that leaves us with 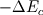 only. only.
- When density changes but cross section is constant: G is also constant so that both terms are finally equal, and we obtain for the pressure drop 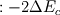 2) Second Method: Generalized Bernoulli's law
2) Second Method: Generalized Bernoulli's law
Let's define hydraulic head, which represents the energy necessary to the fluid motion through piping:
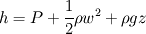
Generalized Bernoulli's law yields in:
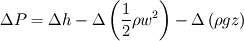
We recognize:
a) 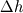 : Head loss due to friction
b) 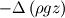 : Pressure drop due to gravity
But then, what is 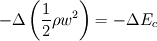 ?? It is indeed pressure drop due to acceleration of the fluid, in the case where the channel is not heated. For the heating channel, the factor 2 is missing!!
CONCLUSION: My opinion is that Bernoulli's law is applicable only for incompressible flows. Yet, when the fluid is heated, 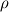 changes so that we cannot really speak about incompressibility. changes so that we cannot really speak about incompressibility.
Do you see any mistake in my formulas or reasoning? Thank you for reading me.
Jérôme |

