A roughness-dependent model
From CFD-Wiki
(Difference between revisions)
(→Kinematic Eddy Viscosity) |
(→Kinematic Eddy Viscosity) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | == | + | ==Two-equation eddy viscosity model== |
| - | Two-equation model | + | <table width="70%"><tr><td> |
<math> | <math> | ||
\nu _t = C_{\mu} {{k^2 } \over \varepsilon } | \nu _t = C_{\mu} {{k^2 } \over \varepsilon } | ||
| - | </math> | + | </math></td><td width="5%">(1)</td></tr></table> |
| - | where: <math> C_{\mu} = 0.09 </math> | + | where: |
| + | <math> C_{\mu} = 0.09 </math> | ||
| - | One-equation model | + | ==One-equation eddy viscosity model== |
| + | <table width="70%"><tr><td> | ||
<math> | <math> | ||
| - | \nu _t = | + | \nu _t = k^{{1 \over 2}} l |
| - | </ | + | </math></td><td width="5%">(2)</td></tr></table> |
| - | Algebraic model: | + | ==Algebraic eddy viscosity model== |
| + | <table width="70%"><tr><td> | ||
| + | <math> | ||
| + | \nu _t(y) = {C_{\mu}}^{{1 \over 4}} l_m(y) k^{{1 \over 2}}(y) | ||
| + | </math></td><td width="5%">(3)</td></tr></table> | ||
| + | <math>l_m</math> is the mixing length. | ||
| + | |||
| + | where: | ||
| + | <table width="70%"><tr><td> | ||
<math> | <math> | ||
| - | k^{{1 \over 2}} = {1 \over {C_{\mu}}^{1 | + | k^{{1 \over 2}}(y) = {1 \over {C_{\mu}}^{{1 \over 4}}} u_\tau e^{\frac{-y}{A}} |
| - | </math> | + | </math></td><td width="5%">(4)</td></tr></table> |
| + | <math>u_\tau </math> is the shear velocity | ||
| + | and: | ||
| + | <table width="70%"><tr><td> | ||
| + | <math> | ||
| + | l_m(y) = \kappa \left( A - \left(A - y_0\right) e^{\frac{-(y-y_0)}{A}} \right) | ||
| + | </math></td><td width="5%">(5)</td></tr></table> | ||
| + | <math>\kappa = 0.4</math>, <math>y_0</math> is the hydrodynamic roughness | ||
| + | |||
| + | therefore: | ||
| + | <table width="70%"><tr><td> | ||
| + | <math> | ||
| + | \nu _t(y) = \kappa \left( A - \left(A - y_0\right) e^{\frac{-(y-y_0)}{A}} \right) | ||
| + | u_\tau e^{\frac{-y}{A}} | ||
| + | </math></td><td width="5%">(6)</td></tr></table> | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
Revision as of 14:57, 19 June 2007
Contents |
Two-equation eddy viscosity model
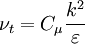 | (1) |
where:
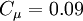
One-equation eddy viscosity model
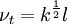 | (2) |
Algebraic eddy viscosity model
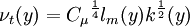 | (3) |
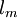 is the mixing length.
is the mixing length.
where:
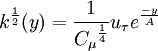 | (4) |
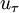 is the shear velocity
is the shear velocity
and:
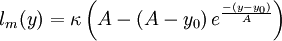 | (5) |
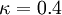 ,
, 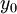 is the hydrodynamic roughness
is the hydrodynamic roughness
therefore:
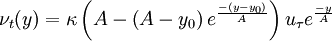 | (6) |
References
- Absi, R. (2006), "A roughness and time dependent mixing length equation", Journal of Hydraulic, Coastal and Environmental Engineering, Japan Society of Civil Engineers, (Doboku Gakkai Ronbunshuu B), Vol. 62, No. 4, pp.437-446.
