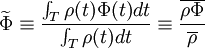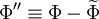Favre averaging
From CFD-Wiki
Let 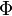 be any dependent variable. This variable can be decomposed into a fluctuating part
be any dependent variable. This variable can be decomposed into a fluctuating part 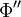 and mean part
and mean part 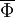 using a density weighted average in the following way:
using a density weighted average in the following way:
|
| (1) |
|
|
Favre averaging is sometimes used in compressible flow to separate turbulent fluctuations from the mean-flow. In most cases it is not necessary to use Favre averaging though, since turbulent fluctuations most often do not lead to any signigicant fluctuations in density. In that case the more simple Reynolds averaging can be used. Only highly compressible flows and hypersonic flows is it necassary to perform the more complex Favre averaging.
Favre averaging can be used to derive the Favre averaged Navier-Stokes equations.