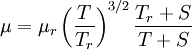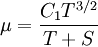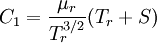Sutherland's law
From CFD-Wiki
In 1893 William Sutherland, an Australian physicist, published a relationship between the absolute temperature, 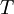 , of an ideal gas and its dynamic visocity,
, of an ideal gas and its dynamic visocity, 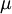 , based on kinetic theory of ideal gases and an idealized intermolecular-force potential. This formula, often called Sutherland's law, is still commonly used and most often gives fairly accurate results with an error less than a few percent over a wide range of temperatures. Sutherland's law can be expressed as:
, based on kinetic theory of ideal gases and an idealized intermolecular-force potential. This formula, often called Sutherland's law, is still commonly used and most often gives fairly accurate results with an error less than a few percent over a wide range of temperatures. Sutherland's law can be expressed as:
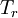 is a reference temperature.
is a reference temperature.
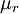 is the viscosity at the
is the viscosity at the 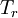 reference temperature
reference temperature
- S is the Sutherland temperature
Some authors instead express Sutherland's law in the following form:
Comparing the formulas above the 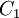 constant can be written as:
constant can be written as:
References
- Sutherland, W. (1893), "The viscosity of gases and molecular force", Philosophical Magazine, S. 5, 36, pp. 507-531 (1893).