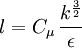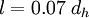Turbulence length scale
From CFD-Wiki
(Added explicit pipe-flow estimation formula) |
m (Turbulent length scale moved to Turbulence length scale) |
Revision as of 17:27, 6 May 2006
The turbulence length scale, 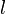 , is a physical quantity describing the size of the large energy containing eddies in a turbulent flow.
, is a physical quantity describing the size of the large energy containing eddies in a turbulent flow.
The turbulent length scale is often used to estimate the turbulent properties on the inlets of a CFD simulation. Since the turbulent length scale is a quantity which is intuitively easy to relate to the physical size of the problem it is easy to guess a reasonable value of the turbulent length scale. The turbulent length scale should normally not be larger than the dimension of the problem, since that would mean that the turbulent eddies are larger than the problem size.
In the k-epsilon model the turbulent length scale can be computed as:
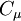 is a model constant which in the standard version of the k-epsilon model has a value of 0.09.
is a model constant which in the standard version of the k-epsilon model has a value of 0.09.
Estimating the turbulent length scale
It is common to set the turbulent length scale to a certain percentage of a typical dimension of the problem. For example, at the inlet to a turbine stage a typical turbulent length scale could be say 5% of the channel height. In grid-generated turbulence the turbulent length scale is often set to something close to the size of the grid bars.
Fully developed pipe flow
In pipe flows the turbulent length scale can be estimated from the hydraulic diameter. In fully developed pipe flow the turbulent length scale is 7% of the hydraulic diameter (in the case of a circular pipe the hydraulic diameter is the same as the diameter of the pipe). Hence:
Where 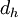 is the hydraulic diameter.
is the hydraulic diameter.