
 |
Quote:
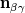 is the normal vector to the gas/liquid interface. In your problem, I will say it depends. If you have an immiscible interface between your two fluids. Yes, you can go for a Volume of Fluid solver as a starting point. is the normal vector to the gas/liquid interface. In your problem, I will say it depends. If you have an immiscible interface between your two fluids. Yes, you can go for a Volume of Fluid solver as a starting point. |
Dear FOAMer,
I have imported StarCCM+ mesh to openfoam 5.0 and quality of mesh was also good. The CCM mesh is trimmed mesh with polyhedral cells. The flow simulation for interFoam with species transport equation (Haroun formulation)diverges after some iterations. Below is report of the checkMesh. Help for resolving this issue would be appreciated. Thanks in advance ******************************* Create time Create polyMesh for time = 0 Time = 0 Mesh stats points: 2709670 faces: 7273254 internal faces: 6550582 cells: 2217107 faces per cell: 6.23508 boundary patches: 10 point zones: 0 face zones: 1 cell zones: 1 Overall number of cells of each type: hexahedra: 1558763 prisms: 17795 wedges: 1051 pyramids: 73 tet wedges: 51 tetrahedra: 184093 polyhedra: 455281 Breakdown of polyhedra by number of faces: faces number of cells 4 4 5 43 6 76272 7 247451 8 4264 9 70800 10 3318 11 356 12 16481 13 700 14 204 15 35328 16 60 Checking topology... Boundary definition OK. Cell to face addressing OK. Point usage OK. Upper triangular ordering OK. Face vertices OK. Number of regions: 1 (OK). Checking patch topology for multiply connected surfaces... Patch Faces Points Surface topology flow:period1 110302 113851 ok (non-closed singly connected) flow:sheet1 229147 166554 ok (non-closed singly connected) flow:sheet2 228457 166118 ok (non-closed singly connected) flow:outg 9532 9665 ok (non-closed singly connected) flow:wallt 9576 9998 ok (non-closed singly connected) flow:period2 110292 113851 ok (non-closed singly connected) flow:inl 5071 5594 ok (non-closed singly connected) flow:wallb 10551 11107 ok (non-closed singly connected) flow:outl 5792 6040 ok (non-closed singly connected) flow:ing 3952 4069 ok (non-closed singly connected) Checking geometry... Overall domain bounding box (-0.0133625 -0.013 -0.0851) (0.0133628 0.013 0.007) Mesh (non-empty, non-wedge) directions (1 1 1) Mesh (non-empty) directions (1 1 1) Boundary openness (4.18881e-14 -2.88815e-15 1.82866e-17) OK. Max cell openness = 2.78469e-16 OK. Max aspect ratio = 9.20971 OK. Minimum face area = 1.10391e-11. Maximum face area = 6.4e-07. Face area magnitudes OK. Min volume = 5.01959e-16. Max volume = 5.12e-10. Total volume = 3.4427e-05. Cell volumes OK. Mesh non-orthogonality Max: 57.8894 average: 11.7876 Non-orthogonality check OK. Face pyramids OK. Max skewness = 3.2775 OK. Coupled point location match (average 0) OK. Mesh OK. End |
Quote:
Hello Cyp, I am trying to simulate a single bubble movement in a solution of water and sugar with interIsoFoam solver, OF2112. I modified the solver and coupled the density, surface tension and viscosity of solution to the concentration of sugar which is different in various parts of the domain. In order to solve the distribution of sugar (a passive scalar) in the geometry, I added a new equation to the solver as below: fvScalarMatrix CEqn ( fvm::ddt(C) + fvm::div(phi, C) - fvm::laplacian(dc,C) == fvOptions(C) ); CEqn.relax(); fvOptions.constrain(CEqn); CEqn.solve(); fvOptions.correct(C); Now, the problem is, sugar concentration penetrates inside the bubble which is not correct. I would like to know how can I prevent sugar entering the bubble? I would be more than happy if you share your opinion with me. |
a question
Quote:
Hello Astrodan, I am trying to simulate a single bubble movement in a solution of water and sugar with interIsoFoam solver, OF2112. I modified the solver and coupled the density, surface tension and viscosity of solution to the concentration of sugar which is different in various parts of the domain. In order to solve the distribution of sugar (a passive scalar) in the geometry, I added a new equation to the solver as below: fvScalarMatrix CEqn ( fvm::ddt(C) + fvm::div(phi, C) - fvm::laplacian(dc,C) == fvOptions(C) ); CEqn.relax(); fvOptions.constrain(CEqn); CEqn.solve(); fvOptions.correct(C); Now, the problem is, sugar concentration penetrates inside the bubble which is not correct. I would like to know how can I prevent sugar entering the bubble? I would be more than happy if you share your opinion with me. |
| All times are GMT -4. The time now is 01:04. |