Reynolds stress model (RSM)
From CFD-Wiki
(→Equations) |
|||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
== Equations == | == Equations == | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Reynolds stress model involves calculation of the individual Reynolds stresses, <math>\overline{u'_iu'_j}</math> , using differential transport equations. The individual Reynolds stresses are then used to obtain closure of the Reynolds-averaged momentum equation. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The exact transport equations for the transport of the Reynolds stresses, <math>\overline{u'_iu'_j}</math> , may be written as follows: | ||
== Model constants == | == Model constants == | ||
Revision as of 21:38, 16 May 2006
Contents |
Introduction
The Reynold's stress model (RSM) is a higher level, elaborate turbulence model. It is usually called a Second Order Closure. This modelling approach originates from the work by [Launder (1975)]. In RSM, the eddy viscosity approach has been discarded and the Reynolds stresses are directl computed. The exact Reynolds stress transport equation accounts for the directional effects of the Reynolds stress fields.
Equations
The Reynolds stress model involves calculation of the individual Reynolds stresses, 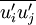 , using differential transport equations. The individual Reynolds stresses are then used to obtain closure of the Reynolds-averaged momentum equation.
, using differential transport equations. The individual Reynolds stresses are then used to obtain closure of the Reynolds-averaged momentum equation.
The exact transport equations for the transport of the Reynolds stresses, 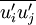 , may be written as follows:
, may be written as follows:
Model constants
Model variants
Performance, applicability and limitations
Implementation issues
References
Launder, B. E., Reece, G. J. and Rodi, W. (1975), "Progress in the Development of Reynolds Stress Turbulent Closure", Journal of Fluid Mechanics, Vol. 68, pp. 537-566.
