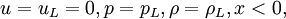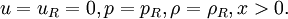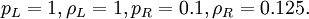Shock tube problem
From CFD-Wiki
(Difference between revisions)
m (Reverted edits by C4tc4Tsitc (Talk) to last version by Jola) |
|||
| (4 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | + | '''Shock tube problem''' is a special case of [[Riemann problem]] with velocities on both sides of discontinuity set to zero. It is often used as a test case for validation of numerical codes, because analytical solutions are available.The initial condition is given by | |
| - | :<math> u | + | :<math>u=u_L=0 , p=p_L , \rho=\rho_L, x<0,</math> |
| - | :<math> u | + | :<math>u=u_R=0 , p=p_R , \rho=\rho_R, x>0.</math> |
| - | + | ||
| - | |||
| - | : | + | A well-known special case is the Sod problem (Sod, 1978) with initial conditions |
| - | + | :<math>p_L=1, \rho_L=1, p_R=0.1, \rho_R=0.125.</math> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
Latest revision as of 14:18, 19 December 2008
Shock tube problem is a special case of Riemann problem with velocities on both sides of discontinuity set to zero. It is often used as a test case for validation of numerical codes, because analytical solutions are available.The initial condition is given by
A well-known special case is the Sod problem (Sod, 1978) with initial conditions