Baldwin-Barth model
From CFD-Wiki
Contents |
Kinematic Eddy Viscosity
Turbulence Reynolds Number
Closure Coefficients and Auxilary Relations
References
- Wilcox, D.C. (2004), Turbulence Modeling for CFD, ISBN 1-928729-10-X, 2nd Ed., DCW Industries, Inc.
- Baldwin, B.S. and Barth, T.J. (1990), A One-Equation Turbulence Transport Model for High Reynolds Number Wall-Bounded Flows, NASA TM 102847.

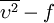 model
model
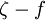 model
model
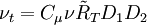
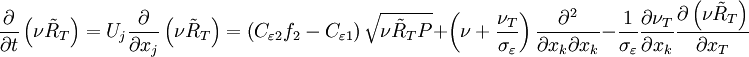
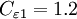
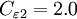
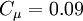
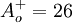
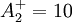
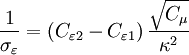
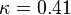
![P = \nu _T \left[ {\left( {{{\partial U_i } \over {\partial x_j }} + {{\partial U_j } \over {\partial x_i }}} \right){{\partial U_i } \over {\partial x_j }} - {2 \over 3}{{\partial U_k } \over {\partial x_k }}{{\partial U_k } \over {\partial x_k }}} \right]](/W/images/math/b/6/6/b666d03659876d1416b6e0b381b908f4.png)
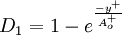
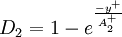
![f_2 = {{C_{\varepsilon 1} } \over {C_{\varepsilon 2} }} + \left( {1 - {{C_{\varepsilon 1} } \over {C_{\varepsilon 2} }}} \right)\left( {{1 \over {\kappa y^ + }} + D_1 D_2 } \right)\left[ {\sqrt {D_1 D_2 } + {{y^ + } \over {\sqrt {D_1 D_2 } }}\left( {{{D_2 } \over {A_o^ + }}e^{{{ - y^ + } \over {A_o^ + }}} + {{D_1 } \over {A_2^ + }}e^{{{ - y^ + } \over {A_2^ + }}} } \right)} \right]](/W/images/math/8/b/a/8ba1c0c35101cba858d27adc8e7ebe78.png)